1. Terminology
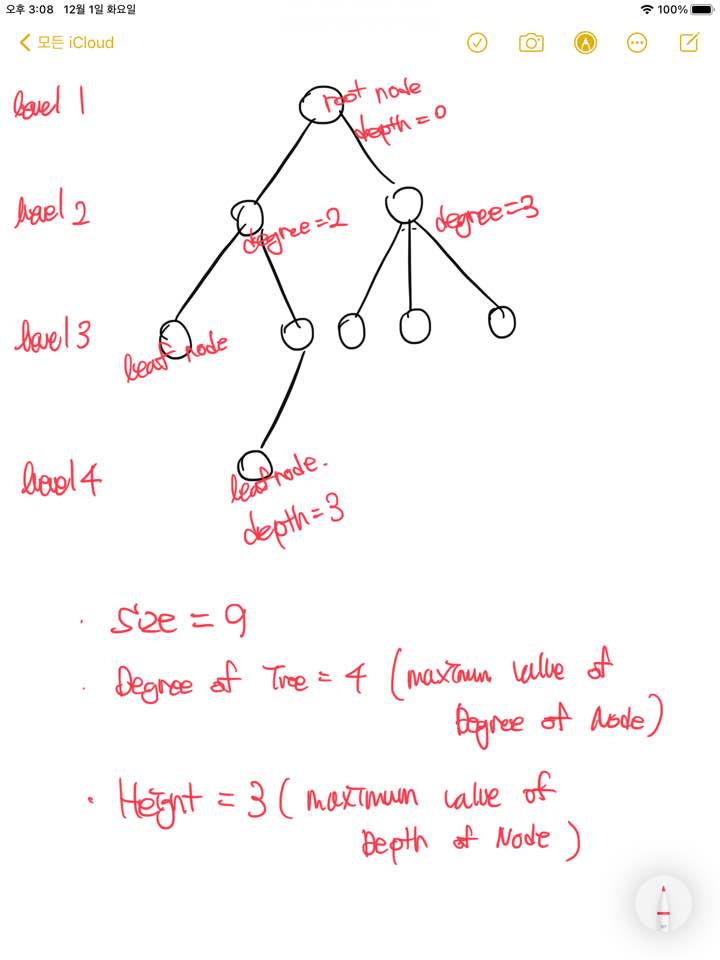
1) Degree : # of child the node has 2) Size : total # of node in tree
3) Depth : # of edge that need to pass from root node(>=0)
4) Height : maximum value of depth
5) Level : set of node at same level
2. Binary Tree
Tree의 각 Node가 최대 2개의 Children Node를 가지는 Tree 자료구조
* number of node in tree = n, height of tree = h 일때
→ 2h + 1 ≤ n ≤ 2^(h+1)-1
1) Compelete Binary Tree : 완전이진트리
마지막 level을 제외하고 모든 level이 완전히 채워져 있으며, 마지막 level의 모든 노드는 가능한 한 가장 왼쪽에 있도록 둔 Tree 자료구조
2) Threaded Binary Tree
- NULL link는 left-child일 때 inorder-processor node을 가리키고, right-childe일 때 inorder-successor node를 가리키는 Tree 자료구조
- 이 때의 NULL link를 Thread라 한다.
3. Heap
최대값 혹은 최소값을 찾아낸 연산을 최적화한 완전이진트리 자료구조
* priority_queue : heap 구조를 이용한 queue
* O(logN)
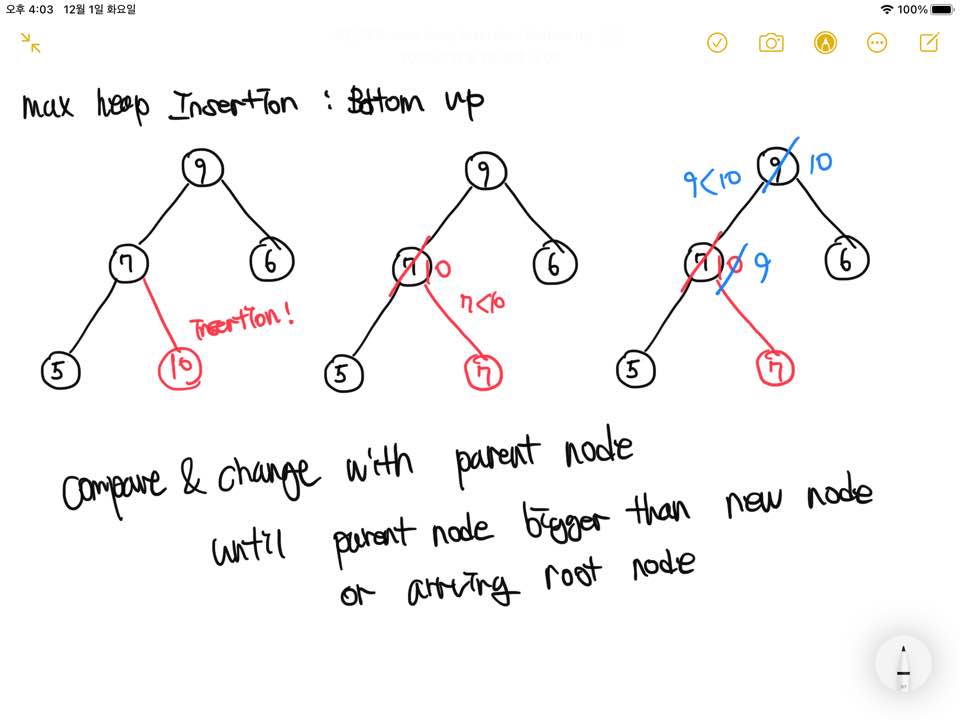
1) Insertion
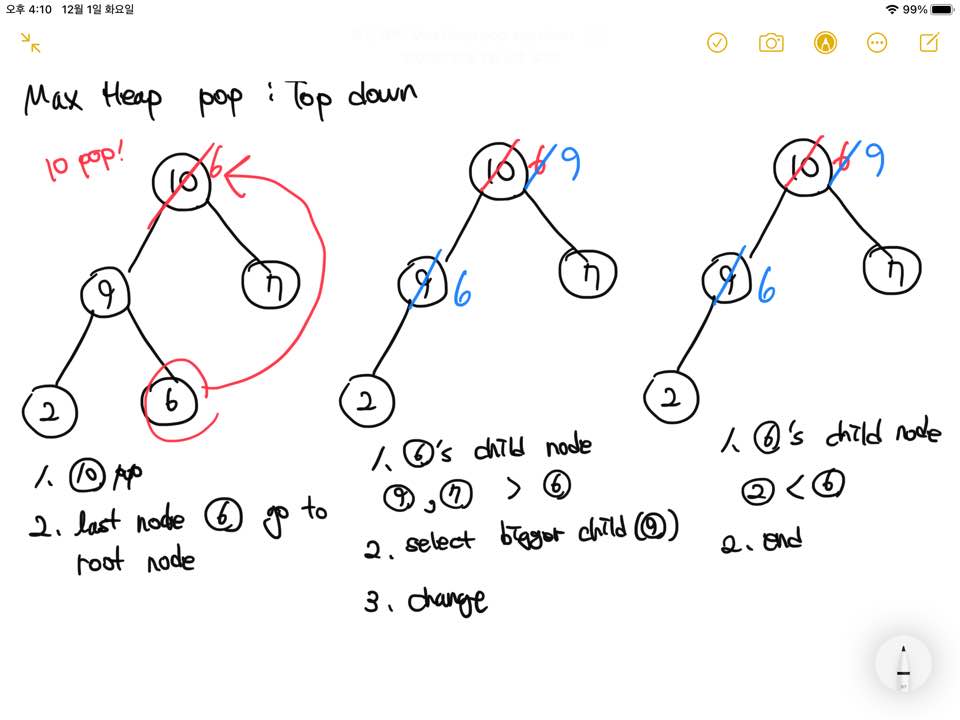
2) Deletion
4. Binary Search Tree : 이진 탐색 트리
이진탐색의 효율적인 탐색 능력을 유지하고 삽입, 삭제 연산의 효율을 늘리기 위해 이진탐색(binary search)과 연결리스트(linked list)를 결합한 Tree 자료구조
* 완전이진트리는 아니기 때문에 Node가 한쪽으로만 치우친 경우 O(h)의 시간 복잡도를 가질 수 있다.
1) Property
- 중복되는 값을 갖는 노드는 없어야 한다.
- 각 노드의 왼쪽 서브트리의 노드는 해당 노드보다 작은 값을 갖는다.
- 각 노드의 오른쪽 서브트리의 노드는 해당 노드보다 큰 값을 갖는다.
- 트리 내 모든 서브트리도 이진 탐색 트리이다.
- 이진 탐색 트리를 Inorder traversal하면 정렬되어 출력된다.
2) Insertion
- Top-down으로 탐색하며 같은 값이 있을 경우는 return false;
- 적절한 위치를 찾았다면 원래 있던 노드의 parent와 연결하고
- 원래 있던 노드를 크기에 따라 삽입한 노드의 left 혹은 right child로 연결
3) Deletion
- 삭제할 값을 가진 Node 탐색
- 경우에 따라 3가지 방법으로 처리
case 1 : // no children
free(node);
case 2 : // one child
parent_node->left = node->left; // or right
free(node);
case 3 : // both children
tmp = t->right;
while(tmp->left != NULL)
tmp = tmp->left; // tmp : node has maximun value in subtree
t->data = tmp->data;
t->right = deletion(tmp->data); // tmp를 위로 올렸으니 삭제해주어야 한다.
5. Forest
하나 이상의 트리로 이루어진 disjoint set(서로소 집합)
각 트리를 하나의 root node로 묶으면 트리..
'CS > 자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [자료구조] 3. Graph : MST, 최단거리, Union-Find (0) | 2020.12.03 |
|---|---|
| [자료구조] 1. Array, Pointer, Stack, Queue, LinkedList (0) | 2020.12.01 |
